SSTs: Difference between revisions
BrianNaess (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (101 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) = | = Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) = | ||
==What are Sea Surface Temperatures (SST) and how are they measured?== | |||
[[File:SST.png|left|thumb|350px|Average Sea Surface Temperature 2011 <ref><ins>http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/indicators/oceans/sea-surface-temp.html</ins></ref>]] | |||
Sea surface temperature is a measure of the energy created by the motion of water molecules on the top layer of the ocean, or the near-surface layer. SSTs vary primarily with latitude but other factors can also affect it. Temperatures are measured between 10 micrometers below the surface with infrared bands and 1 millimeter below the surface with microwave bands using a radiometer.<ref name="PO.DAAC.">Sea Surface Temperature. NASA, n.d. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. <ins>http://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/SeaSurfaceTemperature</ins></ref> Before the 1980s, SST was measured with instruments on shorelines, ships, and buoys, however this was not the most precise or accurate way of measuring. Currently, the bulk of SSTs are measured by remote sensing from satellites, which measure electromagnetic radiation produced by the motion of charged particles. The motion of the charged particle produces electromagnetic radiation and the amplitude of the infrared and microwave wavelengths vary with temperature, which is sensed by the satellites and recorded. Even with these new ways of measuring SST, there are still some floating instruments in the ocean that measure temperature, too. <ref name="PO.DAAC.">Sea Surface Temperature. NASA, n.d. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. <ins>http://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/SeaSurfaceTemperature</ins></ref> | |||
==Why and how are sea surface temperatures rising?== | |||
;Natural [[File:OceanSST.png|right|thumb|350px|Heat Exchange between Atmosphere and Ocean <ref name="bottleneck">Smith, Murray, Craig Stevens, Mike Harvey, and Kim Currie. "The Ocean Surface: The Greenhouse Bottleneck." Homepage. N.p., n.d. Web. 16 Apr. 2014.</ref>]] | |||
:There is natural heat exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere. The ocean is warmed directly from the sun as solar radiation is absorbed by the water and also from contact with the warmer atmosphere. As the ocean water absorbs the atmosphere's excess heat, it becomes warmer and the temperature gradient reverses. Heat is therefore given back to the atmosphere<ref name="Gordon">Gordon, Arnold. "The Climate System." Ocean-Atmosphere Coupling. N.p., 2004. Web. 16 Apr. 2014. <ins>http://eesc.columbia.edu/courses/ees/climate/lectures/o_atm.html</ins></ref>. | |||
:Dominant atmospheric factors driving ocean temperature include wind speed, air temperature, cloudiness, and humidity; dominant oceanic factors include heat transport by currents and vertical mixing. Fluctuations in sea surface temperatures vary with the seasons.<ref name="griffis">Griffis, Roger B., and Jennifer Howard. Oceans and Marine Resources in a Changing Climate: A Technical Input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment. Washington: Island, 2013. Print.</ref> | |||
;Anthropogenic | |||
:Human activities are causing increased concentrations of carbon dioxide to enter the atmosphere, which traps heat and increases atmospheric temperature. As the atmosphere heats up, the temperature gradient between the ocean and atmosphere lessens and heat can't leave the ocean to go back to the atmosphere. | |||
;Feedback Loops | |||
: The relationship between ocean-atmosphere heat exchanges and global weather and climate patterns can be explained by feedback loops. | |||
:As an example, in the case of thermal expansion, given an equal mass, the total volume of ocean waters decrease when ocean temperatures drop and expand when temperatures increase. Due to this property, when sea surface temperatures increase, sea surface volume increases leading to sea surface level increases. | |||
:Positive Feedback: warming of sea surface temperatures leads to increased ice melting and evaporation and increased humidity creates more intense storms, more extreme precipitation, and wind events. Some areas because of increased evaporation will experience intense surface drying increasing the risk of flooding when intense storms occur. <ref name="griffis"></ref> | |||
==What impact does this have on Coral Reefs?== | |||
Increased sea surface temperatures leads to coral [[bleaching]], which is a stress response that causes the coral to expel their zooxanthellae or lose algal pigmentation. Corals are very sensitive to temperature changes, confirmed by the research indicating that bleaching can be triggered when the thermal condition is as little as 1 Celsius higher than the mean summer maximum. <ref>Peñaflor, E. L., W. J. Skirving, A. E. Strong, S. F. Heron, and L. T. David. "Sea-surface Temperature and Thermal Stress in the Coral Triangle over the past Two Decades." Coral Reefs 28.4 (2009): 841-50. Web.</ref> There is, according to a different study, evidence emerging of possible thermal thresholds in the range of 30-32 Celsius for some physiological processes of coral reef organisms. <ref>Lough, J. M. "Small Change, Big Difference: Sea Surface Temperature Distributions for Tropical Coral Reef Ecosystems, 1950–2011." Journal of Geophysical Research 117.C9 (2012): n. pag. Web.</ref> If the coral is stressed by temperatures outside of this range, certain physiological processes suffer decreased function. In research conducted from June to October 2005, satellite-based sea surface temperature observations from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) detected a large region of warming ocean temperatures that reached a maximum anomaly of +1.2°C vs. the long-term mean when averaged across all Caribbean reef sites. In several locations in the oceanic regions with increased temperatures, coral mortality exceeded 50%. Along with coral bleaching due to increased sea surface temperatures, decreased processes of coral physiology resulted in a loss of resistance to pathogenic disease and an increased abundance of microbial pathogens <ref>Eakin, C. Mark, Jessica A. Morgan, Scott F. Heron, et al. "Caribbean Corals in Crisis: Record Thermal Stress, Bleaching, and Mortality in 2005." Ed. Tamara Natasha Romanuk. PLoS ONE 5.11 (2010): Web.</ref> This research confirms that increasing sea surface temperatures have a damaging impact on corals beyond bleaching including disease. | |||
For another impact of increasing sea surface temperatures on coral reefs, please visit [[SSTFlooding|The Potential Link Between Sea Surface Temperatures and Flooding]] | |||
[[File:temp_increase.jpg|thumb|350px|left|Increasing Sea Surface Temperatures <ref>http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/indicators/oceans/sea-surface-temp.html</ref>]] | |||
==What are some predictions in the scientific community in response to current trends?== | |||
Two scientific studies were analyzed to yield both positive and negative data regarding coral reef adaptation in response to increasing sea surface temperatures. | |||
The first scientific study was measuring poleward expansion potential of the coral reef in response to rising sea surface temperatures. The study found that the speed of coral range expansion could reach up to 14 km/year if the reefs were expanding in a region of poleward current flows. Typically coral reefs expand at a rate of 5km/year. While the study yields promising results for future coral expansion into marine environments with a more suitable temperature range, this expansion is only possible given the condition of poleward currents pushing the coral's expansion. <ref>Yamano, Hiroya, Kaoru Sugihara, and Keiichi Nomura. "Rapid Poleward Range Expansion of Tropical Reef Corals in Response to Rising Sea Surface Temperatures." Geophysical Research Letters 38.4 (2011): Web.</ref> | |||
The second scientific study sought to measure the impact of global warming, which directly increases sea surface temperatures through convection, on coral reefs. The study results concluded that an increase of 2 degrees Celsius global mean warming would result in a long-term degradation of all coral reef ecosystems, without a change in thermal tolerance. That is if the temperature were to increase by 2 degrees Celsius, without any adaptive measures the coral reef worldwide would suffer bleaching, stressed physiological processes, and death over the long-term. An increase of 1.5 degrees Celsius global mean warming would result in 89% of all coral reef ecosystems suffering long-term degradation if unable to adequately adapt to increased temperatures. In order to maintain 50% of the coral reef cells, the global mean temperature could rise no more than 1.2 degrees Celsius. This study indicates a serious need for either widespread coral adaptation to increasing sea surface temperatures or extensive limits on sea surface temperature increases to prevent the long-term degradation of coral reef ecosystems. <ref>Frieler, K., M. Meinshausen, A. Golly, M. Mengel, K. Lebek, S. D. Donner, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. "Limiting Global Warming to 2 °C Is Unlikely to save Most Coral Reefs." Nature Climate Change 3.2 (2012): 165-70. Web. </ref> | |||
=== How Much Have Oceans Warmed? === | |||
A recent study looked at sclerosponge carbonate skeletons and found several surprising results <ref name="sclerosponge">McCulloch, M.T., Winter, A., Sherman, C.E. et al. 300 years of sclerosponge thermometry shows global warming has exceeded 1.5 °C. Nat. Clim. Chang. 14, 171–177 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-023-01919-7</ref>: | |||
* "industrial-era warming began in the mid-1860s" | |||
* "global warming was already 1.7 ± 0.1 °C above pre-industrial levels by 2020" | |||
* warming that was "0.5 °C higher than IPCC estimates, with 2 °C global warming projected by the late 2020s, nearly two decades earlier than expected" | |||
The study looked at "[live]specimens ... collected from the Caribbean at depths between 33 and 91 [meters] in an area that they thought was "providing a more stable, representative record of upper surface ocean temperatures." <ref name="sclerosponge" /> | |||
==What are some things we can do to slow down rising Sea Surface Temperatures and their effects?== | |||
*Reduce Carbon Emissions and pollutants, especially since it causes ocean [[acidification]] | |||
*Increase protection for coral to mitigate other threats and make it less vulnerable with marine protected areas [[MPAs]] | |||
*Lower the amount of nutrient overloading | |||
*Increase vegetation cover to prevent sediment runoff | |||
== Notes == | |||
<references /> | |||
Latest revision as of 10:26, 28 February 2024
Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs)
What are Sea Surface Temperatures (SST) and how are they measured?
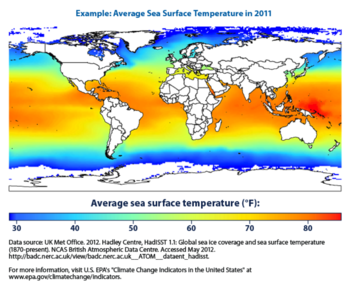
Sea surface temperature is a measure of the energy created by the motion of water molecules on the top layer of the ocean, or the near-surface layer. SSTs vary primarily with latitude but other factors can also affect it. Temperatures are measured between 10 micrometers below the surface with infrared bands and 1 millimeter below the surface with microwave bands using a radiometer.[2] Before the 1980s, SST was measured with instruments on shorelines, ships, and buoys, however this was not the most precise or accurate way of measuring. Currently, the bulk of SSTs are measured by remote sensing from satellites, which measure electromagnetic radiation produced by the motion of charged particles. The motion of the charged particle produces electromagnetic radiation and the amplitude of the infrared and microwave wavelengths vary with temperature, which is sensed by the satellites and recorded. Even with these new ways of measuring SST, there are still some floating instruments in the ocean that measure temperature, too. [2]
Why and how are sea surface temperatures rising?
- Natural
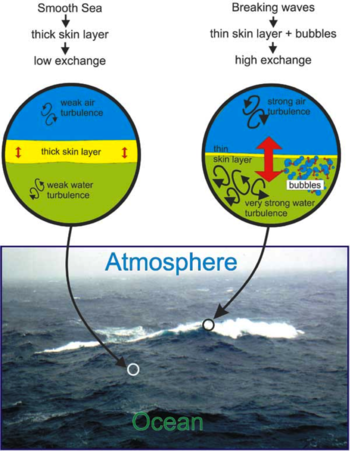
Heat Exchange between Atmosphere and Ocean [3] - There is natural heat exchange between the ocean and the atmosphere. The ocean is warmed directly from the sun as solar radiation is absorbed by the water and also from contact with the warmer atmosphere. As the ocean water absorbs the atmosphere's excess heat, it becomes warmer and the temperature gradient reverses. Heat is therefore given back to the atmosphere[4].
- Dominant atmospheric factors driving ocean temperature include wind speed, air temperature, cloudiness, and humidity; dominant oceanic factors include heat transport by currents and vertical mixing. Fluctuations in sea surface temperatures vary with the seasons.[5]
- Anthropogenic
- Human activities are causing increased concentrations of carbon dioxide to enter the atmosphere, which traps heat and increases atmospheric temperature. As the atmosphere heats up, the temperature gradient between the ocean and atmosphere lessens and heat can't leave the ocean to go back to the atmosphere.
- Feedback Loops
- The relationship between ocean-atmosphere heat exchanges and global weather and climate patterns can be explained by feedback loops.
- As an example, in the case of thermal expansion, given an equal mass, the total volume of ocean waters decrease when ocean temperatures drop and expand when temperatures increase. Due to this property, when sea surface temperatures increase, sea surface volume increases leading to sea surface level increases.
- Positive Feedback: warming of sea surface temperatures leads to increased ice melting and evaporation and increased humidity creates more intense storms, more extreme precipitation, and wind events. Some areas because of increased evaporation will experience intense surface drying increasing the risk of flooding when intense storms occur. [5]
What impact does this have on Coral Reefs?
Increased sea surface temperatures leads to coral bleaching, which is a stress response that causes the coral to expel their zooxanthellae or lose algal pigmentation. Corals are very sensitive to temperature changes, confirmed by the research indicating that bleaching can be triggered when the thermal condition is as little as 1 Celsius higher than the mean summer maximum. [6] There is, according to a different study, evidence emerging of possible thermal thresholds in the range of 30-32 Celsius for some physiological processes of coral reef organisms. [7] If the coral is stressed by temperatures outside of this range, certain physiological processes suffer decreased function. In research conducted from June to October 2005, satellite-based sea surface temperature observations from the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) detected a large region of warming ocean temperatures that reached a maximum anomaly of +1.2°C vs. the long-term mean when averaged across all Caribbean reef sites. In several locations in the oceanic regions with increased temperatures, coral mortality exceeded 50%. Along with coral bleaching due to increased sea surface temperatures, decreased processes of coral physiology resulted in a loss of resistance to pathogenic disease and an increased abundance of microbial pathogens [8] This research confirms that increasing sea surface temperatures have a damaging impact on corals beyond bleaching including disease.
For another impact of increasing sea surface temperatures on coral reefs, please visit The Potential Link Between Sea Surface Temperatures and Flooding
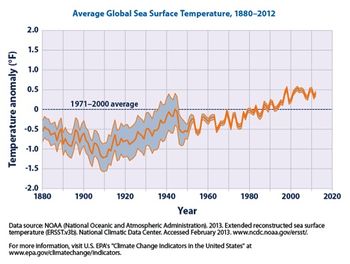
What are some predictions in the scientific community in response to current trends?
Two scientific studies were analyzed to yield both positive and negative data regarding coral reef adaptation in response to increasing sea surface temperatures.
The first scientific study was measuring poleward expansion potential of the coral reef in response to rising sea surface temperatures. The study found that the speed of coral range expansion could reach up to 14 km/year if the reefs were expanding in a region of poleward current flows. Typically coral reefs expand at a rate of 5km/year. While the study yields promising results for future coral expansion into marine environments with a more suitable temperature range, this expansion is only possible given the condition of poleward currents pushing the coral's expansion. [10]
The second scientific study sought to measure the impact of global warming, which directly increases sea surface temperatures through convection, on coral reefs. The study results concluded that an increase of 2 degrees Celsius global mean warming would result in a long-term degradation of all coral reef ecosystems, without a change in thermal tolerance. That is if the temperature were to increase by 2 degrees Celsius, without any adaptive measures the coral reef worldwide would suffer bleaching, stressed physiological processes, and death over the long-term. An increase of 1.5 degrees Celsius global mean warming would result in 89% of all coral reef ecosystems suffering long-term degradation if unable to adequately adapt to increased temperatures. In order to maintain 50% of the coral reef cells, the global mean temperature could rise no more than 1.2 degrees Celsius. This study indicates a serious need for either widespread coral adaptation to increasing sea surface temperatures or extensive limits on sea surface temperature increases to prevent the long-term degradation of coral reef ecosystems. [11]
How Much Have Oceans Warmed?
A recent study looked at sclerosponge carbonate skeletons and found several surprising results [12]:
- "industrial-era warming began in the mid-1860s"
- "global warming was already 1.7 ± 0.1 °C above pre-industrial levels by 2020"
- warming that was "0.5 °C higher than IPCC estimates, with 2 °C global warming projected by the late 2020s, nearly two decades earlier than expected"
The study looked at "[live]specimens ... collected from the Caribbean at depths between 33 and 91 [meters] in an area that they thought was "providing a more stable, representative record of upper surface ocean temperatures." [12]
What are some things we can do to slow down rising Sea Surface Temperatures and their effects?
- Reduce Carbon Emissions and pollutants, especially since it causes ocean acidification
- Increase protection for coral to mitigate other threats and make it less vulnerable with marine protected areas MPAs
- Lower the amount of nutrient overloading
- Increase vegetation cover to prevent sediment runoff
Notes
- ↑ http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/indicators/oceans/sea-surface-temp.html
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Sea Surface Temperature. NASA, n.d. Web. 15 Apr. 2014. http://podaac.jpl.nasa.gov/SeaSurfaceTemperature
- ↑ Smith, Murray, Craig Stevens, Mike Harvey, and Kim Currie. "The Ocean Surface: The Greenhouse Bottleneck." Homepage. N.p., n.d. Web. 16 Apr. 2014.
- ↑ Gordon, Arnold. "The Climate System." Ocean-Atmosphere Coupling. N.p., 2004. Web. 16 Apr. 2014. http://eesc.columbia.edu/courses/ees/climate/lectures/o_atm.html
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Griffis, Roger B., and Jennifer Howard. Oceans and Marine Resources in a Changing Climate: A Technical Input to the 2013 National Climate Assessment. Washington: Island, 2013. Print.
- ↑ Peñaflor, E. L., W. J. Skirving, A. E. Strong, S. F. Heron, and L. T. David. "Sea-surface Temperature and Thermal Stress in the Coral Triangle over the past Two Decades." Coral Reefs 28.4 (2009): 841-50. Web.
- ↑ Lough, J. M. "Small Change, Big Difference: Sea Surface Temperature Distributions for Tropical Coral Reef Ecosystems, 1950–2011." Journal of Geophysical Research 117.C9 (2012): n. pag. Web.
- ↑ Eakin, C. Mark, Jessica A. Morgan, Scott F. Heron, et al. "Caribbean Corals in Crisis: Record Thermal Stress, Bleaching, and Mortality in 2005." Ed. Tamara Natasha Romanuk. PLoS ONE 5.11 (2010): Web.
- ↑ http://www.epa.gov/climatechange/science/indicators/oceans/sea-surface-temp.html
- ↑ Yamano, Hiroya, Kaoru Sugihara, and Keiichi Nomura. "Rapid Poleward Range Expansion of Tropical Reef Corals in Response to Rising Sea Surface Temperatures." Geophysical Research Letters 38.4 (2011): Web.
- ↑ Frieler, K., M. Meinshausen, A. Golly, M. Mengel, K. Lebek, S. D. Donner, and O. Hoegh-Guldberg. "Limiting Global Warming to 2 °C Is Unlikely to save Most Coral Reefs." Nature Climate Change 3.2 (2012): 165-70. Web.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 McCulloch, M.T., Winter, A., Sherman, C.E. et al. 300 years of sclerosponge thermometry shows global warming has exceeded 1.5 °C. Nat. Clim. Chang. 14, 171–177 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-023-01919-7